The History of Man and its Signs
The original Umbrian civilization was replaced in its first expansion
by the Roman one and already in 220 BC the censor Caio Flaminio started
the building of the via Flaminia to link Roma to the high Adriatic area.
Helvillum Vicus (Fossato di Vico), Suillum (Sigillo), Ad Ensem (Scheggia) - respectively Roman federate center, municipium, and
Statius - were always in the Roman political and cultural orbit first,
and then in the Byzantine one, forming with their territories a piece
of the passage that definitively linked Roma to Ravenna despite the
pressure of the Longobard dukedoms. Castrum Costacciari (Costacciaro) was built by the Town of Gubbio around 1250 to fortify
the eastern town border together with Scheggia; Sigillo and Fossato
instead were part of the territory of Perugia that assured to itself,
thanks to the passage road, the access to the salt market from the
Adriatic Sea.
The archaeological finds linked to the via Flaminia
are of great importance, conserved in antiquarium, and still visible in
their original monumental settlement at the Pontespiano.
The historical centers of the four Towns are of great importance for
their culture and landscape, rich in walls and defensive towers, in
churches, in pictures, in fossils collections, in rare archival
documents.
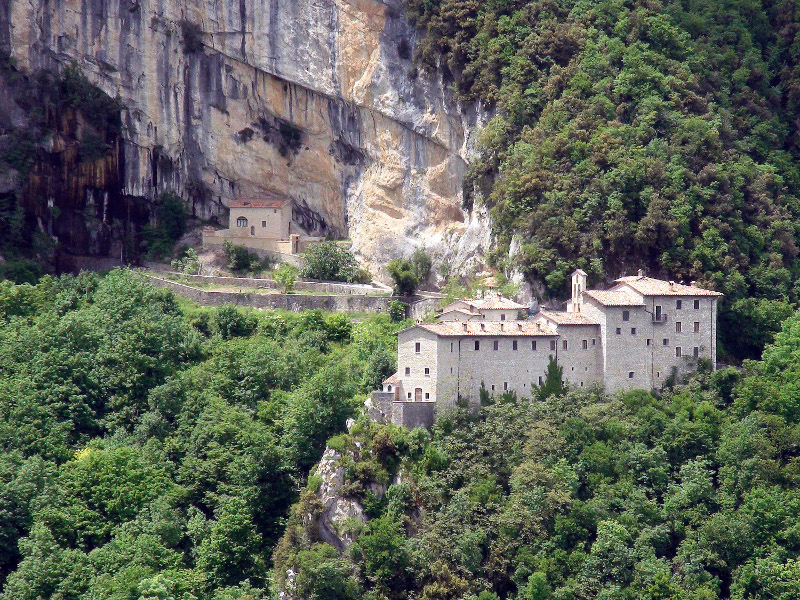
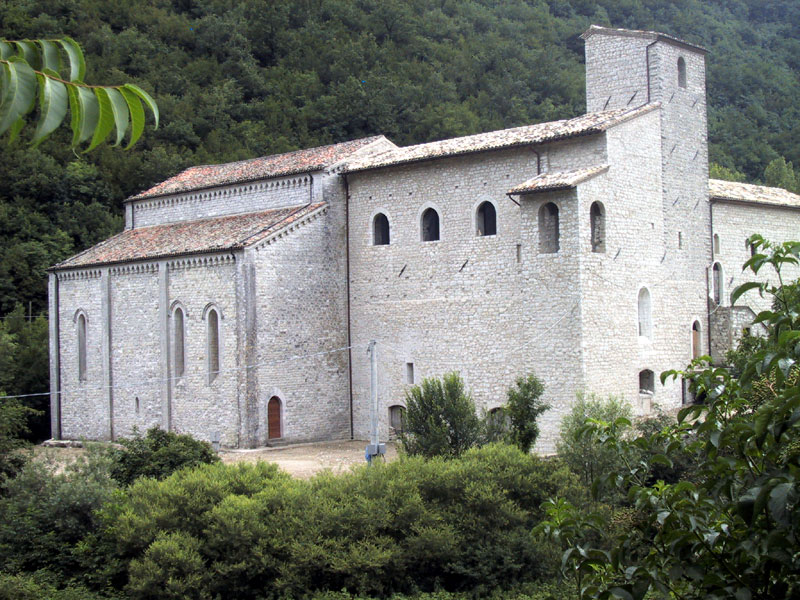
In the northern part of the territory there are several Benedictine and
Camaldolensian abbeys, and among the most important ones: Sant'Emiliano
in Isola Fossara and the Hermitage of San Girolamo in Pascelupo.
- Cultural Heritage, Civil and Religious Monuments (Italian text)