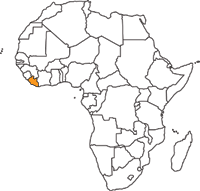
Protected Areas in Liberia
In an attempt to update and revise earlier legislation, especially with respect to wildlife conservation, the Wildlife and National Parks Act was enacted in 1988. This Act identifies a number of protected areas: national park; nature reserve; controlled hunting area; game reserve; and communal forest. In addition, the Act specifies the policies and objectives regarding wildlife conservation in the country.
Forestry Development Authority (FDA)
The Authority is responsible, inter alia, for: establishing a permanent forest estate made up of reserved areas upon which scientific forestry is to be practised; devoting all publicly-owned forests to their most productive use for the good of the whole people considering direct and indirect values; conducting research into the conservation of forests upon which action programmes can be based; and conserving recreational and wildlife resources concurrently with the development of the forestry programme. Under its mandate, the FDA is entitled to create and manage forest reserves and national parks; to adopt rules as required for the implementation of its policies and objectives.
Following 14 years of devastating civil war, there is new hope in Liberia. The signing in August 2003 of the Accra Comprehensive Peace Agreement has led to the establishment of a transitional government and a concerted international effort to help Liberians recover and rebuild their country.
Through its Global Environment Facility Programme, UNDP is supporting the elaboration of a national biodiversity strategy and action plan, and supporting the needed capacity-building and assessment requirements for the three conventions coming out of the 1992 Earth Summit held in Rio de Janeiro: biodiversity, desertification and climate change.
Sources: UNDP – United Nations Development Programme; UNEP-WCMC
|